EventScripts
Mar 6, 2016EventScripts is a fairly advanced Mac OS X utility with a bit of a learning curve. Its job is to run scripts in response to certain events, from things like your external IP address or location changing, to bluetooth devices being seen, or screenshots being taken. You can also talk to it using mobile devices using EventScripts Mobile. It’s a little like Hazel, for system events.
The interface is a bit austere, so to start with it can be a bit overwhelming. Without a doubt the best place to start is the zip of (example scripts)[http://mousedown.net/mouseware/Event_Examples.html], and walkthroughs on the EventScripts site. That should show you how simple the scripts can be, and how to implement your own ideas. In fact, I’ve found my main problem with using it to come up with things to try!
Most of the tricks people online are using it for seem to relate to using bluetooth proximity detection to toggle lights, or unlock their system, but my main use cases is automating moving my laptop between work and home. This article just explains how my current scripts work.
Some examples
My EventScripts config looks like this, with four scripts. I’ll describe each of them in turn.
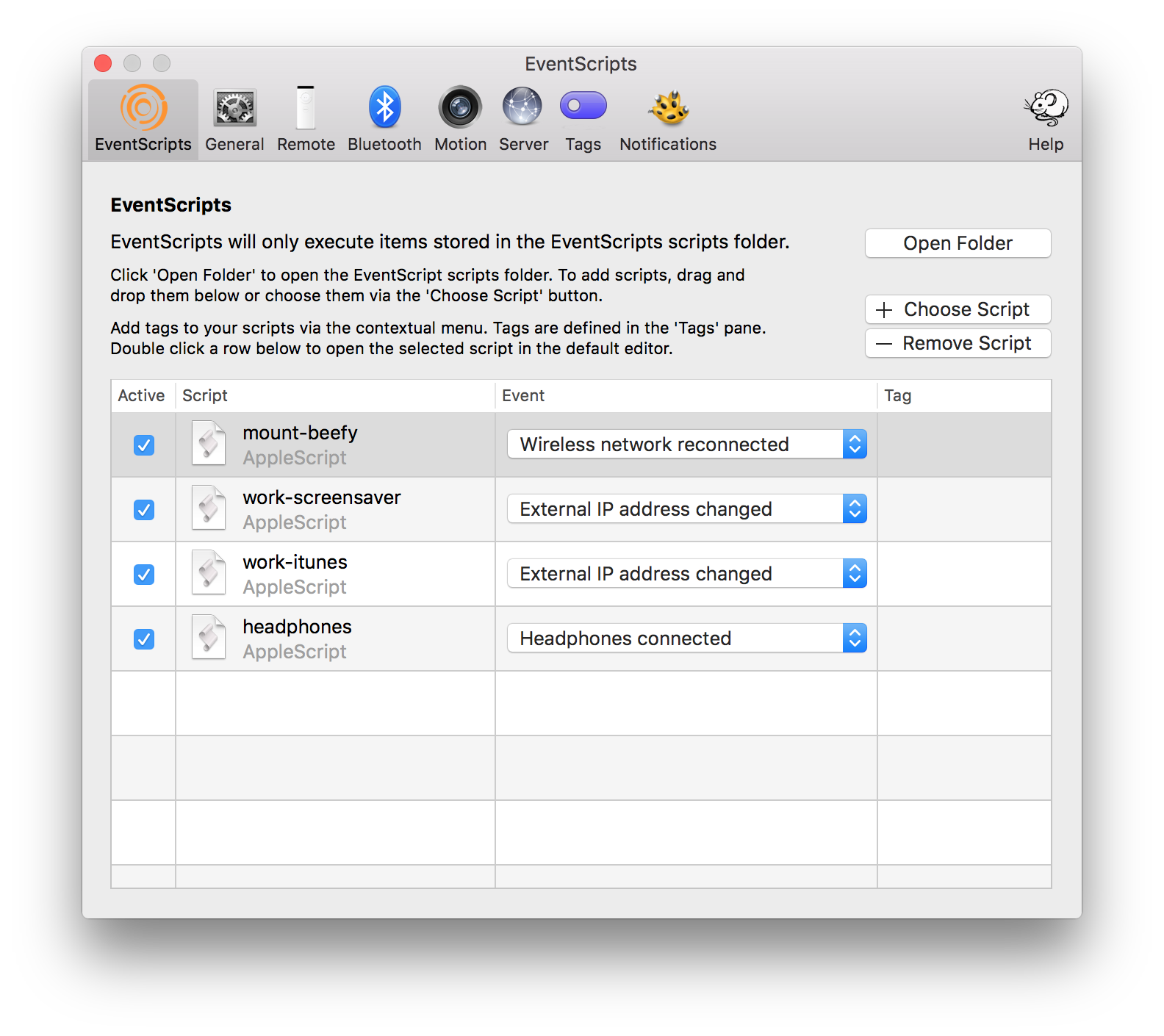
mount-beefy
I have an HP MicroServer (the type that’s almost always available for about £100, after cashback, which I use to server files, and for plex. Because it servers files I like to connect to it when I’m on my home network, so I use the following script:
-- To receive the eventArgs parameter
-- we wrap the script in an on run handler
on run eventArgs
-- every eventArgs record has a trigger property
-- that describes the action that caused the script to be executed
set thisTrigger to (trigger of eventArgs)
if thisTrigger is "Wireless network reconnected" then
-- Get the details about event
set networkName to |SSID| of eventArgs
set oldNetworkName to |previousSSID| of eventArgs
set networkAddress to |BSSID| of eventArgs
if networkName is "Cthulhu" then
tell application "Finder" to mount volume "smb://beefy.local/mpf"
end if
end if
end run
This is triggered by the ‘Wireless network reconnected’ event, which works because I almost always use WiFi to connect to my home network, so when I see the network ‘Cthulhu’, my Mac mounts my home directory using Samba.
One possible tweak would be to have Transmit mount the drive using SFTP, using something like this:
tell application "Transmit"
set myFave to item 1 of (favorites whose name is "My Favorite")
tell current tab of (make new document at end)
connect to myFave with mount
close
end tell
end tell
work-screensaver
This script sets my screensaver interval to 100 seconds, this means my Mac will lock if I leave my desk, no faffing with bluetooth!
-- To receive the eventArgs parameter
-- we wrap the script in an on run handler
on run eventArgs
-- every eventArgs record has a trigger property
-- that describes the action that caused the script to be executed
set thisTrigger to (trigger of eventArgs)
if thisTrigger is "External IP address changed" then
-- Get the details about event
set oldAddress to |previousAddress| of eventArgs
set currentAddress to |ipAddress| of eventArgs
if currentAddress is "NAT IP ADDRESS" then
tell application "System Events" to tell screen saver preferences to set delay interval to 100
end if
end if
end run
This is triggered by the ‘External IP address changed’ event. The currentAddress variable will automatically be set to the systems external IP address, which for most people will be the IP of a device performing natting (your router’s external IP).
I actually also set the delay much higher when I’m at home, using the topmost script, but I edited that line out for clarity.
work-itunes
I got fed up with telling iTunes to stop using my AirPlay devices whenever I get into work, so added this:
-- To receive the eventArgs parameter
-- we wrap the script in an on run handler
on run eventArgs
-- every eventArgs record has a trigger property
-- that describes the action that caused the script to be executed
set thisTrigger to (trigger of eventArgs)
if thisTrigger is "External IP address changed" then
-- Get the details about event
set oldAddress to |previousAddress| of eventArgs
set currentAddress to |ipAddress| of eventArgs
if currentAddress is "NAT IP ADDRESS" then
tell application "iTunes" to set current AirPlay devices to AirPlay device "Computer"
end if
end if
end run
This is my favourite script so far, and it’s also bound to the ‘External IP address changed’ event.
headphones-connected
This simple script disconnects AirPlay when you plug headphones in.
-- To receive the eventArgs parameter
-- we wrap the script in an on run handler
on run eventArgs
tell application "iTunes" to set current AirPlay devices to AirPlay device "Computer"
end run
I haven’t added any logic to reverse this, mainly because I don’t always use AirPlay, so switching it back on won’t always be what I want. This is bound to the ‘Headphone connected’ event.
Wrapping up
Hopfully some of the examples here will be useful to you. I still feel like I’m just scratching the surface of things I could do with it.
For example, each script has access to the event that triggered it, so there’s a lot more you could do with single large scripts. You could probably also save state on disk to help keep track of things, like whether you were using AirPlay before you originally plugged your headphones in.
Future plans include looking into tweaking the max upload rate of Arq when I’m at home, and perhaps automatically switching calendar sets in Fantastical although it has its own location based switching already.
Feel free to share any cool scripts in the comments.